Statistically Valid Variable Importance Assessment through Conditional Permutations
Statistically consistent regression modeling from brain activity recoreded with M/EEG
Summary
(reprinted from abstract)
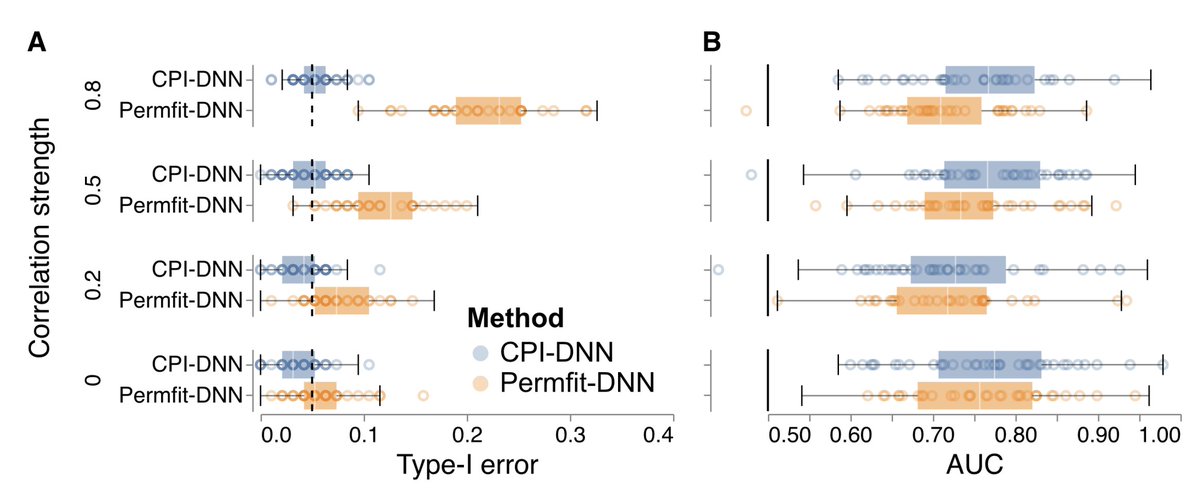
Variable importance assessment has become a crucial step in machine-learning applications when using complex learners, such as deep neural networks, on large-scale data. Removal-based importance assessment is currently the reference approach, particularly when statistical guarantees are sought to justify variable inclusion. It is often implemented with variable permutation schemes. On the flip side, these approaches risk misidentifying unimportant variables as important in the presence of correlations among covariates. Here we develop a systematic approach for studying Conditional Permutation Importance (CPI) that is model agnostic and computationally lean, as well as reusable benchmarks of state-of-the-art variable importance estimators. We show theoretically and empirically that CPI overcomes the limitations of standard permutation importance by providing accurate type-I error control. When used with a deep neural network, CPI consistently showed top accuracy across benchmarks. An experiment on real-world data analysis in a large-scale medical dataset showed that CPI provides a more parsimonious selection of statistically significant variables. Our results suggest that CPI can be readily used as drop-in replacement for permutation-based methods.
(Twitter/X)
Citation
@article{chamma2023statistically,
title={Statistically Valid Variable Importance Assessment through Conditional Permutations},
author={Chamma, Ahmad and Engemann, Denis A and Thirion, Bertrand},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07593},
year={2023}
}